The blood is generally make up of 4 components
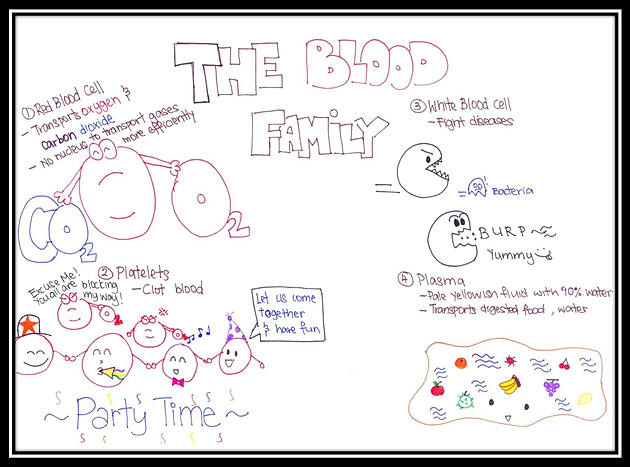
1. Red Blood Cells
Red Blood Cells transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is involved in gaesous exchange in the air sacs of lungs as well as in cells during respiration.
Red blood cell is a special animal cell that contains NO NUCLEUS. Hence it cannot undergo cell division to replicate itself. To ensure continuity of red blood cells, the body made them in the bone marrow.
Red blood cell is bi-concave in shape. Together with its shape and without any nucleus, the red blood cell is able to have higher contact surface area with the gases and hence transport the gases more efficiently.
2. Platelets
The main function of platelets is to clot blood. By clotting blood, we will stop blood flow and preventing excessive blood loss.
When we have a cut or a broken blood vessel, platelets are activated. Fibrin, a network of fibres, is also formed around the platelets. The platelets then clump together to stop blood flow.
3. White Blood Cells
White Blood Cells are our body warriors. They are also part of our immune system to fight dieseases.
There are different types of white blood cells. Some of them targets bacteria or fungi by engulfingthem. Other white blood cells are involved in
- healing of inflammatory sites,
- releasing antibodies to help body to fight dieases and
- killing old and damaged body cellss
White blood cell is also made by the bone marrow.
4. Plasma
Plasma is a pale yellowish fluid made up of 90% water. It is 55% of our blood.
It plays a very important function in transporting digested food, water and waste products.
It also transport hormones and important proteins to maintain the body's fluid balance.
All in all, the blood functions are:
- Transporting oxygen, carbon dioxide, digested food, water and waste products
- Fighting diseases
- Clotting blood
Topic: PSLE Science Upper Block, Circulatory System, Components and Functions of Blood
Comments
Post a Comment